Law Of Multiple Proportions
 The Law Of Multiple Proportions Science
The Law Of Multiple Proportions Science
Law of multiple proportions

The law of multiple proportions states that :
- If two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element which combine with a fixed mass of the first element will always be ratios of small whole numbers.[1]
This is one of the basic laws of stoichiometry used to establish the atomic theory, alongside the law of conservation of mass (matter) and the law of definite proportions. It is sometimes called Dalton's Law after its discoverer, the British chemist John Dalton,[2][1] who published it in the first part of the first volume of his "New System of Chemical Philosophy" (1808).[3]
For example, Dalton knew that the element carbon forms two oxides by combining with oxygen in different proportions. A fixed mass of carbon, say 100 grams, may react with 133 grams of oxygen to produce one oxide, or with 266 grams of oxygen to produce the other. The ratio of the masses of oxygen that can react with 100 grams of carbon is 266:133 = 2:1, a ratio of small whole numbers.[4] Dalton interpreted this result in his atomic theory by proposing (correctly in this case) that the two oxides have one and two oxygen atoms respectively for each carbon atom. In modern notation the first is CO (carbon monoxide) and the second is CO2 (carbon dioxide).
John Dalton first expressed this observation in 1804.[5] A few years previously, the French chemist Joseph Proust had proposed the law of definite proportions, which expressed that the elements combined to form compounds in certain well-defined proportions, rather than mixing in just any proportion; and Antoine Lavoisier proved the law of conservation of mass, which helped out Dalton. Careful study of the actual numerical values of these proportions led Dalton to propose his law of multiple proportions. This was an important step toward the atomic theory that he would propose later that year, and it laid the basis for chemical formulas for compounds.
Another example of the law can be seen by comparing ethane (C2H6) with propane (C3H8). The weight of hydrogen which combines with 1 g carbon is 0.252 g in ethane and 0.224 g in propane. The ratio of those weights is 1.125, which can be expressed as the ratio of two small numbers 9:8.
Limitations
The law of multiple proportions is best demonstrated using simple compounds. For example, if one tried to demonstrate it using the hydrocarbons decane (chemical formula C10H22) and undecane (C11H24), one would find that 100 grams of carbon could react with 18.46 grams of hydrogen to produce decane or with 18.31 grams of hydrogen to produce undecane, for a ratio of hydrogen masses of 121:120, which is hardly a ratio of "small" whole numbers.
The law fails with non-stoichiometric compounds and also doesn't work well with polymers and oligomers.
References
- ^ a b "law of multiple proportions definition". groups.molbiosci.northwestern.edu. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
- ^ Helmenstine, Anne. "Law of Multiple Proportions Problem". 1. Retrieved 31 January 2012.
- ^ Elements and Atoms: Chapter 7 Atoms of Definite Weight: Dalton from Classic Chemistry (Selected Classic Papers from the History of Chemistry) compiled by Carmen Giunta
- ^ Petrucci, Ralph H.; Harwood, William S.; Herring, F. Geoffrey (2002). General chemistry: principles and modern applications (8th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J: Prentice Hall. p. 37. ISBN 978-0-13-014329-7. LCCN 2001032331. OCLC 46872308.
- ^ "law of multiple proportions | chemistry". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 26 October 2017.
Gallery Law Of Multiple Proportions
 Category The Law Of Multiple Proportions Chem230 Wiki Fandom
Category The Law Of Multiple Proportions Chem230 Wiki Fandom
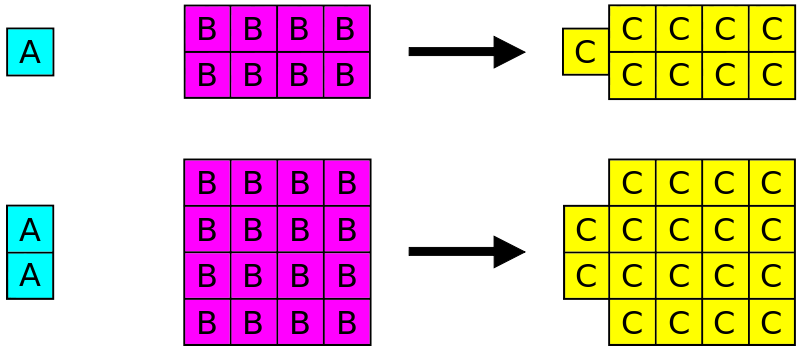 Difference Between Law Of Definite Proportions And Law Of
Difference Between Law Of Definite Proportions And Law Of
 Solution Which Of The Following Sets Ill Chemistry
Solution Which Of The Following Sets Ill Chemistry
 Quiz Worksheet Law Of Multiple Proportions Study Com
Quiz Worksheet Law Of Multiple Proportions Study Com
 Law Of Multiple Proportions Definition Examples Video
Law Of Multiple Proportions Definition Examples Video
 2 2 Fundamental Chemical Laws Apchemwins
2 2 Fundamental Chemical Laws Apchemwins
An Experiment To Illustrate The Law Of Multiple Proportions
 Mass Laws Law Of Conservation Of Mass Law Of Constant
Mass Laws Law Of Conservation Of Mass Law Of Constant
 Lab 1 Law Of Multiple Proportions Che 110 Csudh Studocu
Lab 1 Law Of Multiple Proportions Che 110 Csudh Studocu
 What Is Law Of Conservation Of Mass Law Of Constant
What Is Law Of Conservation Of Mass Law Of Constant
 Multiple Proportions Some Extra Questions
Multiple Proportions Some Extra Questions

 Solved Which Statement Describes The Law Of Multiple Prop
Solved Which Statement Describes The Law Of Multiple Prop
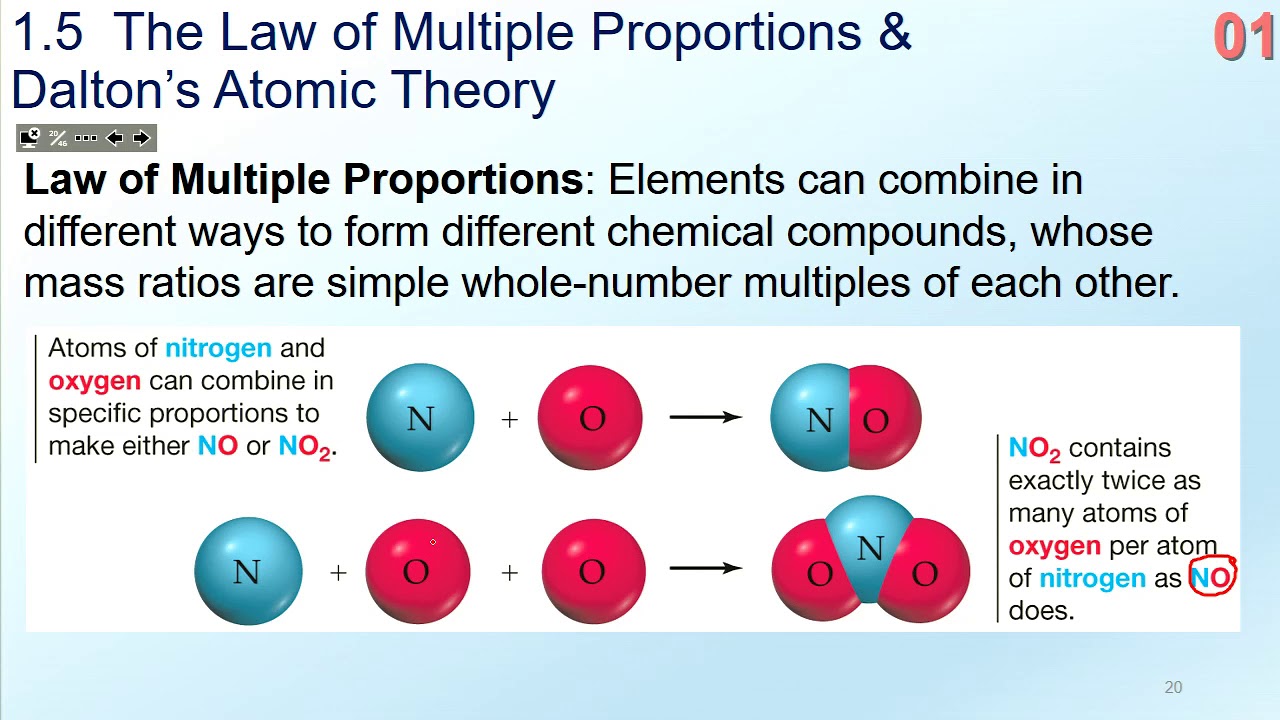 Ch 1 5 Law Of Multiple Proportions Daltons Atomic Theory
Ch 1 5 Law Of Multiple Proportions Daltons Atomic Theory
 The Law Of Definite Proportions Vs The Law Of Multiple
The Law Of Definite Proportions Vs The Law Of Multiple
 Which Of The Following Is An Example Of The Law Of Multiple Proportions A A Sample Of Chlorine Is Found To Contain Three Times As Much Cl 35 As Cl 37 B Two Different Compounds Formed From Carbon And
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of The Law Of Multiple Proportions A A Sample Of Chlorine Is Found To Contain Three Times As Much Cl 35 As Cl 37 B Two Different Compounds Formed From Carbon And
Stephens Chemistry Laws Of Definite And Multiple
Law Of Multiple Proportions Need Method Check Please

0 Response to "Law Of Multiple Proportions"
Post a Comment