Post Stroke Icd 10
 Why You Must Code For Medical Necessity With Icd 10 Webpt
Why You Must Code For Medical Necessity With Icd 10 Webpt
2020 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I63.9

- 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code
- I63.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I63.9 became effective on October 1, 2019.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I63.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 I63.9 may differ.
Applicable To
Type 2 Excludes Help
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here". A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code (I63.9) and the excluded code together.
- transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes (
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G45
- G45 Transient cerebral ischemic attacks and relat...
- G45.0 Vertebro-basilar artery syndrome
- G45.1 Carotid artery syndrome (hemispheric)
- G45.2 Multiple and bilateral precerebral artery syn...
- G45.3 Amaurosis fugax
- G45.4 Transient global amnesia
- G45.8 Other transient cerebral ischemic attacks and...
- G45.9 Transient cerebral ischemic attack, unspecifi...
- G45 Transient cerebral ischemic attacks and relat...
Annotation Back-References
In this context, annotation back-references refer to codes that contain:
- Applicable To annotations, or
- Code Also annotations, or
- Code First annotations, or
- Excludes1 annotations, or
- Excludes2 annotations, or
- Includes annotations, or
- Note annotations, or
- Use Additional annotations
- I00-I99
2020 ICD-10-CM Range I00-I99
Diseases of the circulatory system
Diseases of the circulatory systemType 2 Excludes- certain conditions originating in the perinatal period (P04-P96)
- certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99)
- complications of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (O00-O9A)
- congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00-Q99)
- endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases (E00-E88)
- injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes (S00-T88)
- neoplasms (C00-D49)
- symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified (R00-R94)
- systemic connective tissue disorders (M30-M36)
- transient cerebral ischemic attacks and related syndromes (G45.-)
- I60-I69
2020 ICD-10-CM Range I60-I69
Cerebrovascular diseases
Cerebrovascular diseasesType 1 Excludes- traumatic intracranial hemorrhage (S06.-)
- I63
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I63
Cerebral infarction- 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Includes
- occlusion and stenosis of cerebral and precerebral arteries, resulting in cerebral infarction
Type 2 Excludes
- sequelae of cerebral infarction (I69.3-)
Use Additional
- code, if applicable, to identify status post administration of tPA (rtPA) in a different facility within the last 24 hours prior to admission to current facility (Z92.82)
- Acute ischemic stroke
- Acute ischemic stroke with coma
- Acute lacunar stroke
- Acute stroke, nonatherosclerotic
- Acute thrombotic stroke
- Basal ganglion infarct
- Brain stem infarction
- Cerebellar infarct
- Cerebellar stroke
- Cerebellar stroke syndrome
- Cerebral vascular accident (stroke) <8>
- Cerebrovascular accident
- Cerebrovascular infarction during cardiac surgery
- Infarction of basal ganglia
- Infarction of brain stem
- Infarction of medulla oblongata
- Infarction of posterior cerebral circulation
- Ischemic stroke
- Ischemic stroke with coma
- Ischemic stroke without coma
- Lacunar infarction
- Nonatherosclerotic cerebrovascular accident
- Paralytic stroke
- R.i.n.d. Syndrome
- Reversible ischemic neurologic deficit syndrome
- Stroke
- Thalamic infarct
- Thalamic infarction
- Thrombotic stroke
- A disorder characterized by a sudden loss of sensory function due to an intracranial vascular event.
- A group of pathological conditions characterized by sudden, non-convulsive loss of neurological function due to brain ischemia or intracranial hemorrhages. Stroke is classified by the type of tissue necrosis, such as the anatomic location, vasculature involved, etiology, age of the affected individual, and hemorrhagic vs. Non-hemorrhagic nature. (from Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, pp777-810)
- A stroke is a medical emergency. Strokes happen when blood flow to your brain stops. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. There are two kinds of stroke. The more common kind, called ischemic stroke, is caused by a blood clot that blocks or plugs a blood vessel in the brain. The other kind, called hemorrhagic stroke, is caused by a blood vessel that breaks and bleeds into the brain. "mini-strokes" or transient ischemic attacks (tias), occur when the blood supply to the brain is briefly interrupted.symptoms of stroke are
- sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg (especially on one side of the body)
- sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech
- sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- sudden severe headache with no known cause
- A sudden loss of neurological function secondary to hemorrhage or ischemia in the brain parenchyma due to a vascular event. Infarction or hemorrhage may be demonstrated either directly by imaging, laboratory, or pathologic examination in patients with symptom duration less than 24 hours, or inferred by symptoms lasting greater than or equal to 24 hours (or fatal within 24 hours) that cannot be attributed to another cause. Diagnostic tests include ct scan, mri, angiography, and eeg to locate and evaluate the extent of the hemorrhagic or ischemic damage in the brain parenchyma, coagulation studies, complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and urinalysis.
- An ischemic condition of the brain, producing a persistent focal neurological deficit in the area of distribution of the cerebral arteries.
- In medicine, a loss of blood flow to part of the brain, which damages brain tissue. Strokes are caused by blood clots and broken blood vessels in the brain. Symptoms include dizziness, numbness, weakness on one side of the body, and problems with talking, writing, or understanding language. The risk of stroke is increased by high blood pressure, older age, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, heart disease, atherosclerosis (a build-up of fatty material and plaque inside the coronary arteries), and a family history of stroke.
- Sudden neurologic impairment due to a cerebrovascular disorder, either an arterial occlusion or an intracranial hemorrhage.
- The formation of an area of necrosis in the cerebrum caused by an insufficiency of arterial or venous blood flow. Infarcts of the cerebrum are generally classified by hemisphere (i.e., left vs. Right), lobe (e.g., frontal lobe infarction), arterial distribution (e.g., infarction, anterior cerebral artery), and etiology (e.g., embolic infarction).
- 023 Craniotomy with major device implant or acute complex cns pdx with mcc or chemotherapy implant or epilepsy with neurostimulator
- 024 Craniotomy with major device implant or acute complex cns pdx without mcc
- 061 Ischemic stroke, precerebral occlusion or transient ischemia with thrombolytic agent with mcc
- 062 Ischemic stroke, precerebral occlusion or transient ischemia with thrombolytic agent with cc
- 063 Ischemic stroke, precerebral occlusion or transient ischemia with thrombolytic agent without cc/mcc
- 064 Intracranial hemorrhage or cerebral infarction with mcc
- 065 Intracranial hemorrhage or cerebral infarction with cc or tpa in 24 hours
- 066 Intracranial hemorrhage or cerebral infarction without cc/mcc
- 791 Prematurity with major problems
- 793 Full term neonate with major problems
Convert I63.9 to ICD-9-CM
Code History- 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM)
- 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change
- 2018 (effective 10/1/2017): No change
- 2019 (effective 10/1/2018): No change
- 2020 (effective 10/1/2019): No change
- Accident
- cerebrovascular (embolic) (ischemic) (thrombotic) I63.9
- cerebral I63.9
- craniovascular I63.9
- vascular, brain I63.9
- Deficit - see also Deficiency
- neurologic NEC R29.818
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R29.818
Other symptoms and signs involving the nervous system
- 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code
- ischemic
- reversible (RIND) I63.9
- ischemic
- prolonged reversible ischemic neurologic I63.9 (PRIND)
-
- Infarct, infarction
- PRIND I63.9 (Prolonged reversible ischemic neurologic deficit)
- RIND I63.9 (reversible ischemic neurologic deficit)
- Stroke (apoplectic) (brain) (embolic) (ischemic) (paralytic) (thrombotic) I63.9
ICD-10-CM Codes Adjacent To I63.9
I63.54 Cerebral infarction due to unspecified occlusion or stenosis of cerebellar artery
I63.541 Cerebral infarction due to unspecified occlusion or stenosis of right cerebellar artery
I63.542 Cerebral infarction due to unspecified occlusion or stenosis of left cerebellar artery
I63.543 Cerebral infarction due to unspecified occlusion or stenosis of bilateral cerebellar arteries
I63.549 Cerebral infarction due to unspecified occlusion or stenosis of unspecified cerebellar artery
I63.59 Cerebral infarction due to unspecified occlusion or stenosis of other cerebral artery
I63.6 Cerebral infarction due to cerebral venous thrombosis, nonpyogenic
I63.8 Other cerebral infarction
I63.81 …… due to occlusion or stenosis of small artery
I63.89 Other cerebral infarction
I63.9 Cerebral infarction, unspecified
I65.0 Occlusion and stenosis of vertebral artery
I65.01 Occlusion and stenosis of right vertebral artery
I65.02 Occlusion and stenosis of left vertebral artery
I65.03 Occlusion and stenosis of bilateral vertebral arteries
I65.09 Occlusion and stenosis of unspecified vertebral artery
I65.1 Occlusion and stenosis of basilar artery
I65.2 Occlusion and stenosis of carotid artery
I65.21 Occlusion and stenosis of right carotid artery
I65.22 Occlusion and stenosis of left carotid artery
Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Gallery Post Stroke Icd 10
 Number Of Cases And Proportion Of Hz Diagnoses Icd 10 Codes
Number Of Cases And Proportion Of Hz Diagnoses Icd 10 Codes
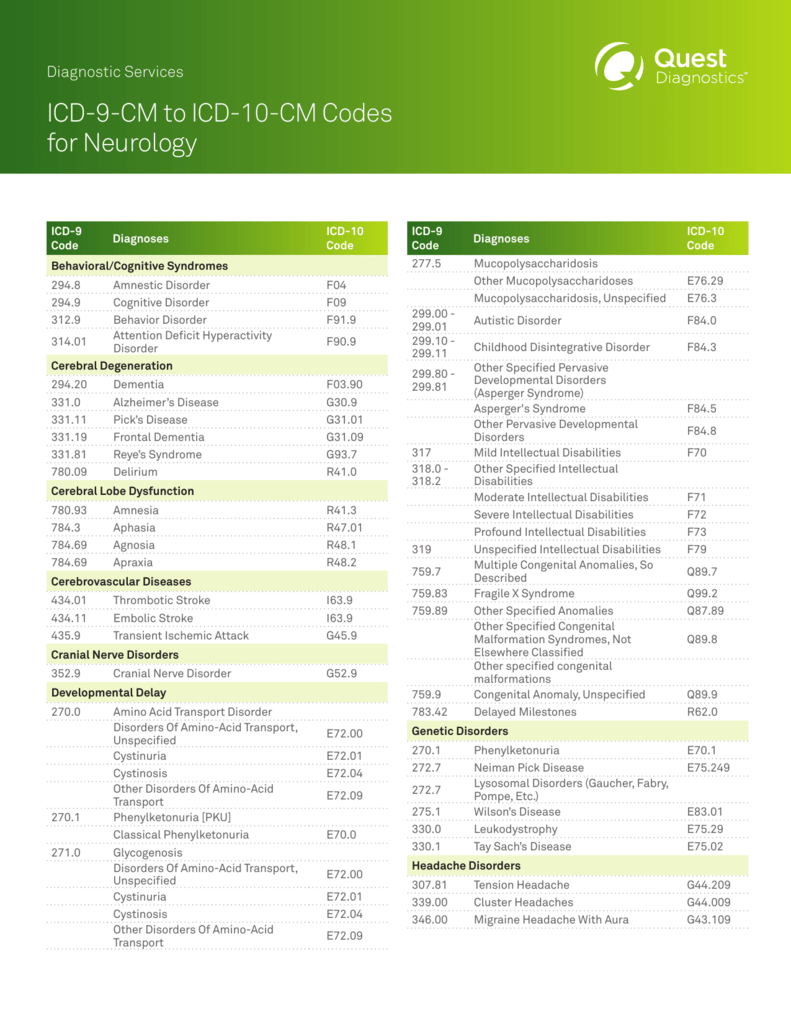 Icd 9 Cm To Icd 10 Cm Codes For Neurology
Icd 9 Cm To Icd 10 Cm Codes For Neurology
 Icd Coding For Epilepsy Past Present And Future A Report
Icd Coding For Epilepsy Past Present And Future A Report
Guide For Icd 10 S And Ambulance Services
 The Little Guy Vs Big Data Is Icd 10 Coding Still Valuable
The Little Guy Vs Big Data Is Icd 10 Coding Still Valuable
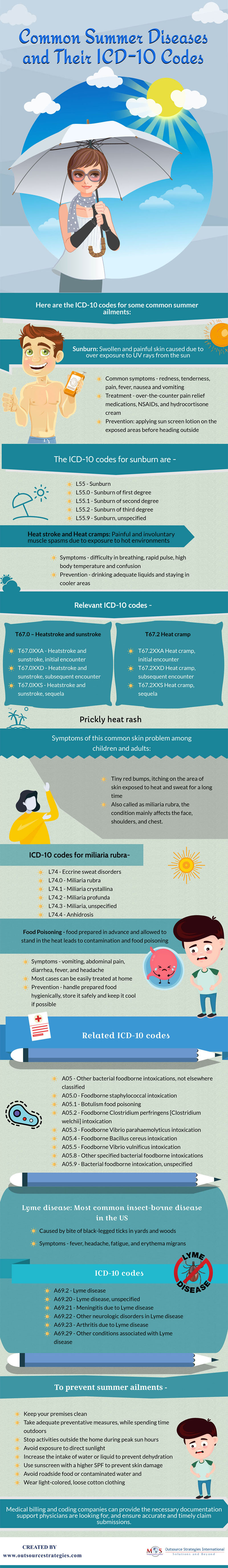 Common Summer Diseases And Their Icd 10 Codes
Common Summer Diseases And Their Icd 10 Codes
 Medical Necessity Icd 10 What Pts Need To Know Webpt
Medical Necessity Icd 10 What Pts Need To Know Webpt
 Increased Risk For Cancer After Stroke At A Young Age
Increased Risk For Cancer After Stroke At A Young Age
Icd 10 Cm General Coding Guidelines
 Education Series Part 2 Common Icd 10 Coding Errors Found
Education Series Part 2 Common Icd 10 Coding Errors Found
 Coding Atrial Fibrillation Using Correct Icd 10 And Cpt Codes
Coding Atrial Fibrillation Using Correct Icd 10 And Cpt Codes
 What You Should Know About Icd 10 Cm Codes Podiatry Today
What You Should Know About Icd 10 Cm Codes Podiatry Today
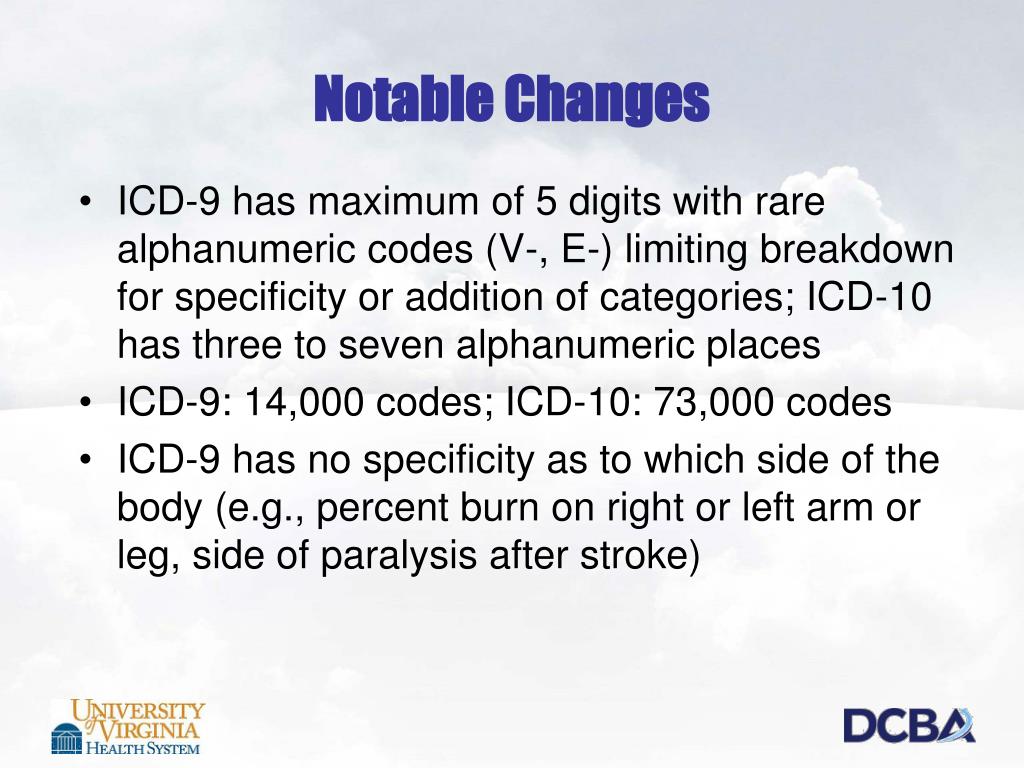 Ppt Value Based Purchasing Changes For Icd 10 And The
Ppt Value Based Purchasing Changes For Icd 10 And The
 Icd Codes For Conditions Leading To Acquired Brain Injury
Icd Codes For Conditions Leading To Acquired Brain Injury
 Comparing Icd 9 To Icd 10 Code Structure And Organization
Comparing Icd 9 To Icd 10 Code Structure And Organization
The Centers For Medicare And Medicaid Services Cms Has
 Fy 2020 Part 1 Icd 10 Cm Codes And Official Guidelines For
Fy 2020 Part 1 Icd 10 Cm Codes And Official Guidelines For
This Is The Full Title Of A Session A Matter Of Principle
 How To Code Sequela Of Cva In Icd 10 Home Health Coding Tip By Pps Plus September 2017
How To Code Sequela Of Cva In Icd 10 Home Health Coding Tip By Pps Plus September 2017
 Finally A Systematic Classification Of Pain The Icd 11
Finally A Systematic Classification Of Pain The Icd 11
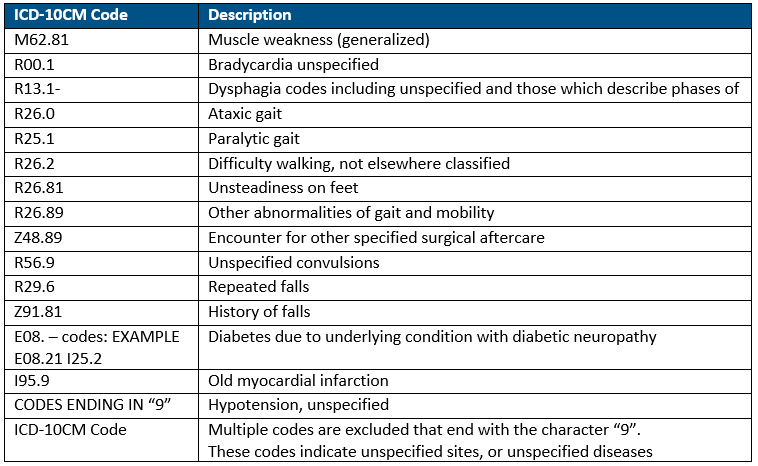





0 Response to "Post Stroke Icd 10"
Post a Comment